We already discussed the fundamental concepts of Apache Cassandra database.We discussed the basic operations with Apache Cassandra from Java. Those operations are read, insert , delete etc. In this chapter we are discussing how a Java object is persisting in Apache Cassandra . Here, we are simply putting all the attribute values of an object against the attribute names in a column family. Each object can be identified with a unique row key.
Inserting Objects into Apache Cassandra using Hector API
Apache Thrift allows us to generate classes to easily communicate with Apache Cassandra from client applications. Let us see an example. This example generates a class Student with two attributes ‘id‘ and ‘name‘.
Generating class using Thrift
The steps are :
1)Download Thrift.exe from Apache Page.
(We are using Thrift 0.9.0 because we are using Thrift libraries 0.9.0 to communicate with Apache Cassandra)
2)Create a directory some where in disk and put the Thrift.exe in it.
(In our case , I created a folder Thrift in D drive)
3)Now create a file with .Thrift extension in the directory created in step 2.
(In our case the file is beans.Thrift)
4)Now put the following as content of beans.Thrift.
#namespace defines package for generated classes
namespace java com.cassandrasamples.beans
struct Student{
1:string id,
2:string name
}
The name space specifies the language and the package
5)Now open a command prompt and go to the thrift directory and execute the command :
thrift-0.9.0.exe -gen java beans.thrift
This generates a class with already mentioned package in the gen-java folder inside thrift directory.
Put the generated class in the corresponding package in work space . In the coming example , we will be using this as a model class.(I am not copying the generated class here.)
Now let us look into the Java client application which inserts few Student objects into Apache Cassandra database. We are using the same key space ‘USERKEYSPACE‘ created already .We need to start Apache Cassandra database and we should include the libraries mentioned there to the work space to run our application.
ObjectInsertSample.java
The Student object has ‘id’ and ‘name’ . We are storing two Student objects in a new column family ‘myColumnFamily‘.Each object is having a unique row key . The Student id is using as row key.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import me.prettyprint.cassandra.serializers.StringSerializer;
import me.prettyprint.hector.api.Cluster;
import me.prettyprint.hector.api.Keyspace;
import me.prettyprint.hector.api.ddl.ColumnFamilyDefinition;
import me.prettyprint.hector.api.ddl.ComparatorType;
import me.prettyprint.hector.api.factory.HFactory;
import me.prettyprint.hector.api.mutation.Mutator;
import com.cassandrasamples.beans.Student;
public class ObjectInsertSample {
Cluster cluster = null;
Keyspace keyspace = null;
public ObjectInsertSample() {
}
public void getConfig() {
cluster = HFactory.getOrCreateCluster("Test Cluster", "localHost:9160");
keyspace = HFactory.createKeyspace("USERKEYSPACE", cluster);
}
public void insert(List
if (null != cluster && null != keyspace) {
ColumnFamilyDefinition columnFamily = HFactory
.createColumnFamilyDefinition("USERKEYSPACE",
"myColumnFamily", ComparatorType.UTF8TYPE);
cluster.addColumnFamily(columnFamily);
StringSerializer stringSerializer = StringSerializer.get();
Mutator
stringSerializer);
for (Student student : studentList) {
Map
Set set = map.entrySet();
Iterator i = set.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) i.next();
mutator.addInsertion(student.getId(), columnFamily
.getName(), HFactory.createStringColumn(entry
.getKey().toString(), entry.getValue().toString()));
System.out.println("Done");
}
mutator.execute();
}
}
}
public Map processKeyValueMap(Student student) {
HashMap returnMap = new HashMap
if (null != student.getId() && null != student.getName()) {
returnMap.put("id", student.getId());
returnMap.put("name", student.getName());
}
return returnMap;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectInsertSample sample = new ObjectInsertSample();
sample.getConfig();
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setId("1");
student1.setName("Bijoy");
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setId("2");
student2.setName("Karthik");
List
students.add(student1);
students.add(student2);
System.out.println("Inserting student records....");
sample.insert(students);
System.out.println("Done...");
}
}
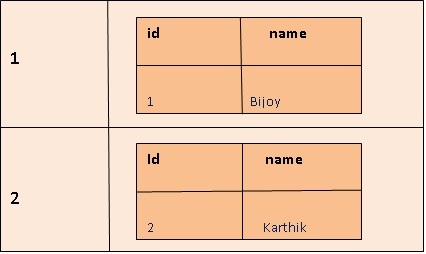
After insertion the column family structure will be like this:
Output
We need to start the Apache Cassandra database and the key space ‘USERKEYSPACE’ should be added as discusses earlier.We should include the libraries discussed there.Now run the application. When insertion is successful , corresponding messages will be displayed .In the next chapter we’ll see how these data is retrieving.
See Related Posts:
Configuring Apache Cassandra in local machine
Inserting data into Apache Cassandra using Java
Reading data from Apache Cassandra using Java
Listing columns in Apache Cassandra using Java